Rust disease on coffee plants causes serious damage. Using products from Sataka Vietnam such as LINSAY, NIKIBUL helps protect plants and increase productivity effectively.
Coffee Rust Disease
Coffee leaf rust is a significant disease that not only causes substantial yield losses but also affects the quality of the final product. Understanding the disease and implementing effective prevention measures will help farmers manage their coffee plantations better, leading to bountiful harvests and improved product quality.
1. Overview of Coffee Leaf Rust Disease
Coffee leaf rust is one of the most common and damaging diseases in the coffee industry. It is caused by the Hemileia vastatrix fungus, primarily targeting coffee leaves, reducing photosynthesis and overall plant health.
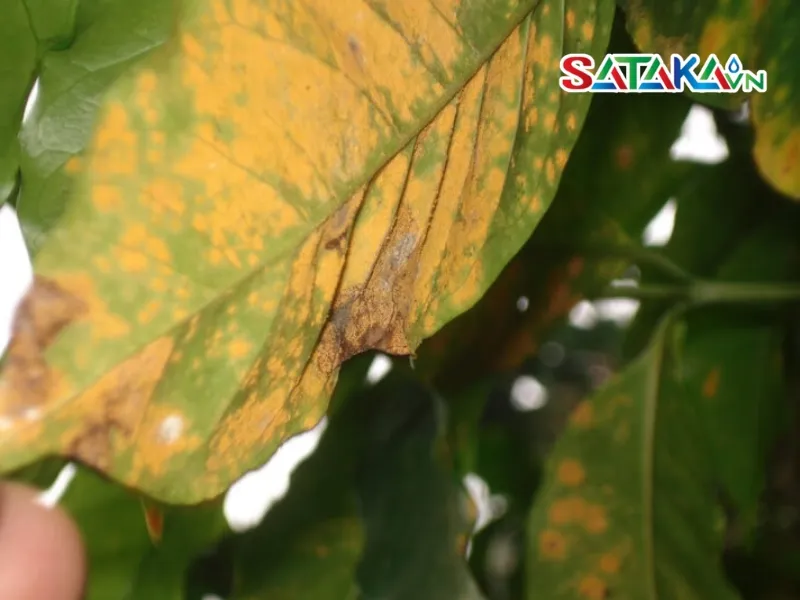

Leaf color of coffee rust disease
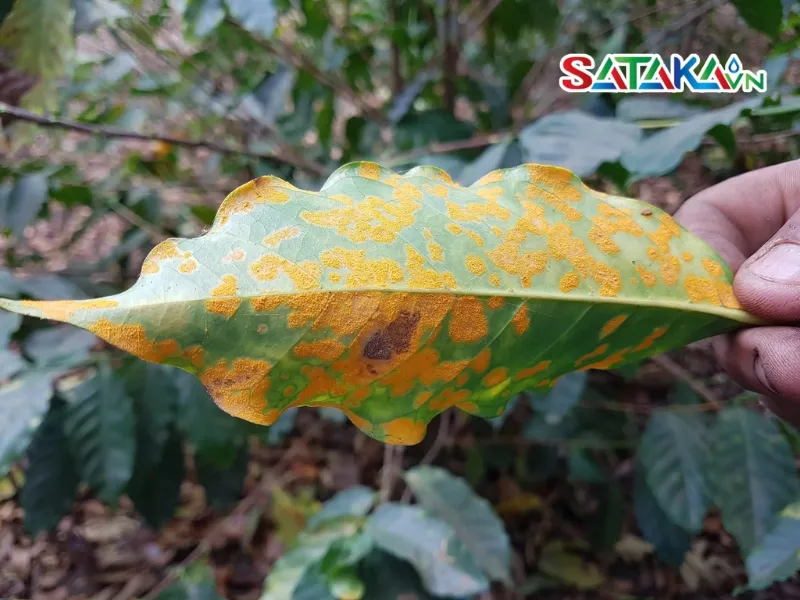
The disease manifests as spots, yellowing, and premature leaf drop, weakening the plant and lowering fruit production. According to a report by the International Coffee Organization (ICO), coffee leaf rust has caused yield losses of 20-30% in affected regions.
2. Conditions for the Development of Coffee Leaf Rust
Coffee leaf rust thrives under specific conditions, particularly related to climate, humidity, and garden management. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting and preventing the disease effectively.
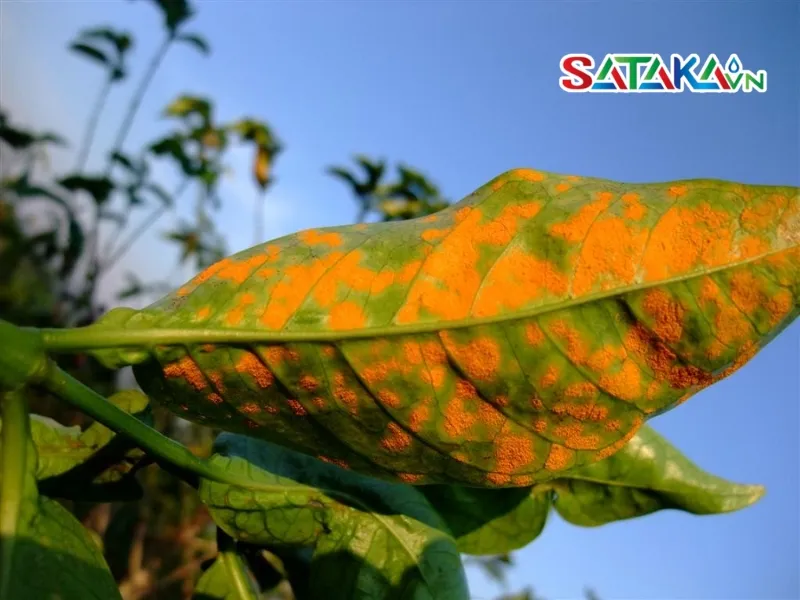

Rust disease in coffee plants often develops very quickly
2.1 Climate and Weather
- Temperature: The Hemileia vastatrix fungus thrives at temperatures between 20-28°C. Temperatures outside this range are less favorable for the fungus's growth and spread.
- Humidity: Wet and humid conditions, such as heavy rainfall or dense fog, create ideal environments for the fungus to flourish.
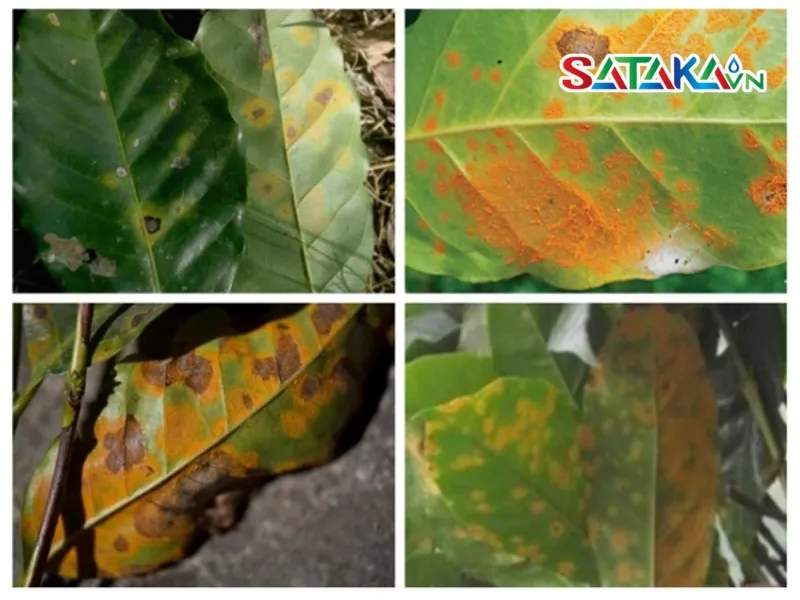

Climate is an important determining factor for coffee rust disease
2.2 Garden Management
- Plant Density: Overcrowded coffee plantations create humid, poorly ventilated environments that encourage fungal growth.
- Plant Care: Poorly maintained coffee plants, improper fertilization, or lack of pruning are more susceptible to the disease. Weak root systems, damaged leaves, and nutrient deficiencies also increase vulnerability.
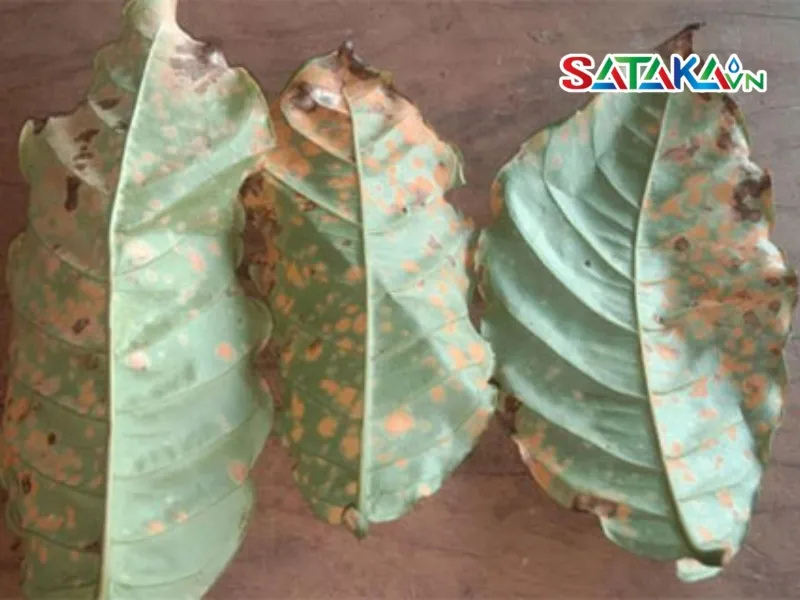

Planting trees at too high a density will spread the disease faster
2.3 Geographic Characteristics
- Altitude: Coffee plantations at altitudes between 600 and 1,200 meters are more prone to leaf rust compared to higher or lower elevations.
3. Main Causes of Coffee Leaf Rust
Coffee leaf rust results from various factors, but the primary cause is the Hemileia vastatrix fungus. This parasitic fungus attacks coffee leaves, causing the characteristic yellow rust spots. Key causes include:
- Hemileia vastatrix: The fungus infects coffee leaves, creating yellow spots that turn brown and spread, reducing the plant's photosynthetic ability.
- Unfavorable Environmental Conditions: High humidity and temperatures, as mentioned, are ideal for the fungus to grow.
- Poor Garden Management: Neglected plantations with insufficient pruning and improper fertilization weaken plants, making them more susceptible.
- Susceptible Coffee Varieties: Some coffee varieties are less resistant to leaf rust. Selecting non-resistant varieties increases the likelihood of infection.
- Spore Transmission: The fungus spores spread easily through wind, rain, and even small animals, leading to widespread outbreaks.

The fungus Hemileia vastatrix is the main cause of rust
4. Symptoms of Coffee Leaf Rust
Recognizing the symptoms of coffee leaf rust early is vital for effective management. Key signs to watch for include:
- Yellow Spots on Leaves: Small yellow spots appear on the underside of leaves. These spots gradually grow and become more prominent.
- Orange Powdery Substance: The upper leaf surface develops an orange or yellow powdery layer, which are the spores of Hemileia vastatrix, capable of spreading to other leaves.
- Premature Leaf Drop: Infected leaves fall earlier than usual, significantly affecting the plant’s photosynthesis and weakening it.
- Dry and Stunted Leaves: Infected leaves dry out, turn brown, and may develop cracks. The plant becomes stunted and struggles to grow and bear fruit.
- Reduced Yield and Bean Quality: Coffee leaf rust reduces the plant’s productivity and bean quality, leading to lower yields and economic losses.
5. Impact of Coffee Leaf Rust
- Reduced Yield: The disease hampers photosynthesis due to premature leaf drop and damaged leaves. According to a FAO study, coffee leaf rust can reduce yields by 20-40%, causing significant crop losses.
- Lower Bean Quality: Infected plants produce underdeveloped beans with inferior weight and quality, making them unsuitable for consumption or export.
- Increased Production Costs: Managing leaf rust requires additional costs for pesticides, spraying, and protective measures, significantly increasing production expenses, especially for small-scale farmers.
- Weakened Plant Growth: Infected plants not only lose leaves but also become stunted and weak, reducing overall growth and resilience.
- Risk of Spread: The fungus spreads quickly via spores, potentially infecting vast cultivation areas if not controlled in time.
- Economic and Social Impact: Coffee is a key economic sector for many countries. Coffee leaf rust negatively affects not only yields but also farmer incomes and national revenues, creating considerable economic and social pressures.
6. Preventing Coffee Leaf Rust
Effective management of coffee leaf rust is essential to protect yields and ensure product quality. Here are some recommended products from Sataka for controlling leaf rust:
LINSAY
A leading pesticide effective against bacteria and viruses that cause coffee leaf rust. With advanced formulation, LINSAY is quickly absorbed by plants, eliminating pathogens efficiently.
NIKIBUL
Highly effective in eradicating fungi responsible for coffee leaf rust, NIKIBUL also enhances the plant’s resistance, promoting healthy growth.
ZINNY 80
A specialized fungicide offering long-lasting protection against leaf rust. ZINNY 80 reduces the risk of disease recurrence in your coffee garden.
MITOP ONE 390SC
This potent fungicide swiftly eliminates fungal spores causing coffee leaf rust. It is safe for plants and environmentally friendly.
AZOXYSTROBIN
Widely used in plant protection, azoxystrobin effectively kills the Hemileia vastatrix fungus while protecting against other pathogens.
Tricyclazole 75% WP
This powder-form pesticide effectively controls and prevents coffee leaf rust by inhibiting fungal growth, helping maintain plant health and productivity.
Raw materials for pesticides from Sataka Vietnam
7. Tips for Using Fungicides
- Always read and follow the instructions on the product label.
- Spray in the early morning or late afternoon for better absorption and minimal impact on plants.
- Rotate different fungicides to prevent the development of fungal resistance.
Effective prevention and control of coffee leaf rust are critical for maintaining yields and product quality. Using high-quality fungicides will help you keep your coffee garden healthy and productive. Visit Sataka's website for more details and to choose the best products for your coffee farm!





