Leaf spot disease on pepper plants is one of the most common diseases and causes serious damage to pepper plants. The following article will provide information about the causes and effective ways to prevent leaf spot disease on pepper plants.
Pepper plants cannot avoid facing various diseases throughout their growth process, and one of the most common and harmful diseases is leaf spot disease on pepper plants. In the following article by Sataka, we will explore leaf spot disease on pepper plants, covering its causes, symptoms, and effective prevention methods.
Leaf spot disease on pepper plants is a common disease caused by fungi or bacteria. This disease primarily affects the leaves of pepper plants, causing damage and making them prone to shedding. Small yellow or brown spots appear on the leaf surface, and if not promptly controlled, the disease will spread rapidly, causing significant harm to the entire plant. Leaf spot disease not only weakens the plant but can also lead to reduced photosynthesis, negatively impacting growth and the quality of pepper products.
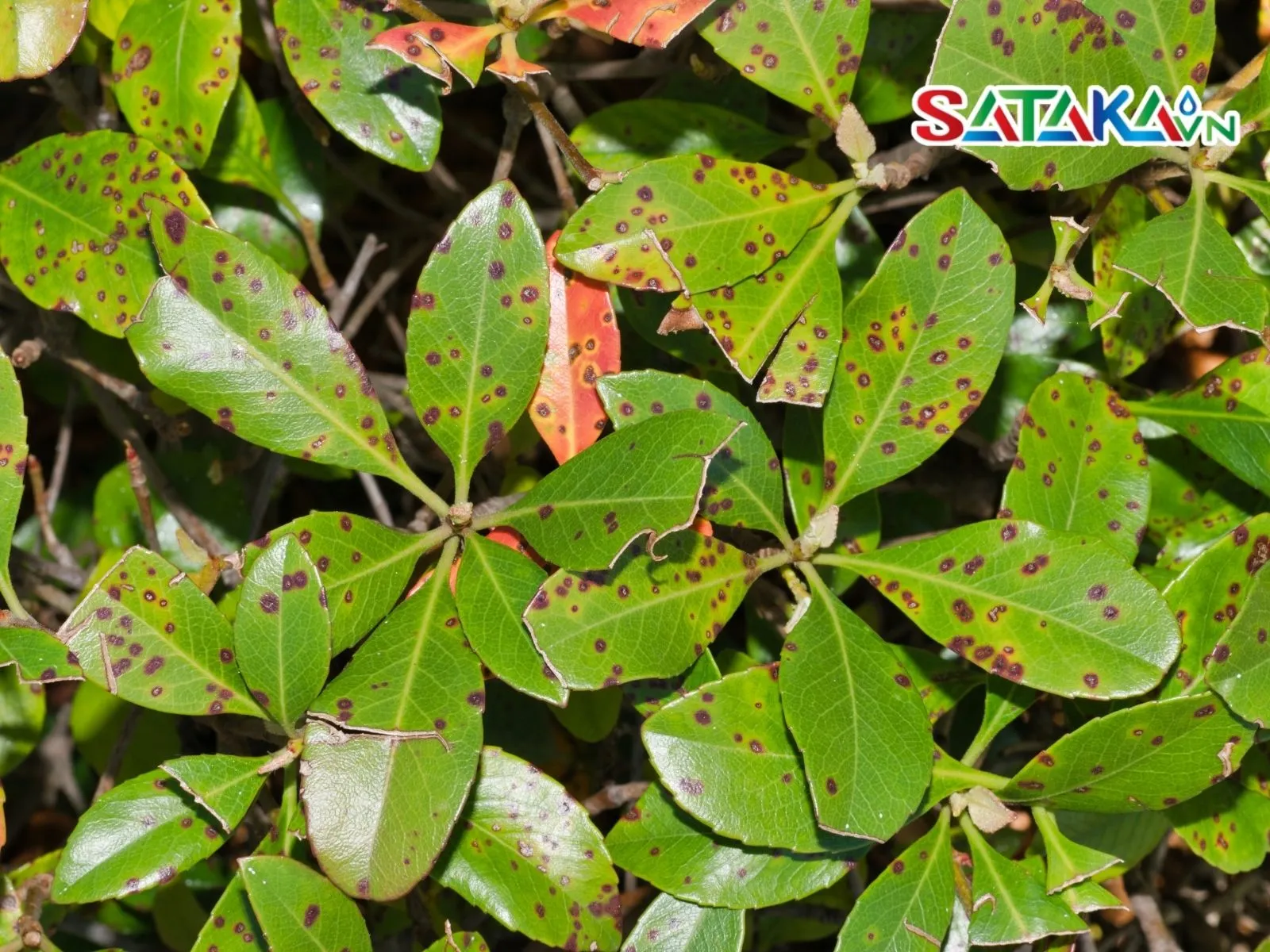

Leaf spot disease on pepper plants
Early detection of leaf spot disease symptoms helps protect pepper plants from future consequences. The most recognizable signs of this disease are the appearance of small spots, initially yellow, which later turn brown or black on the leaves. These spots often start at the leaf edges and gradually spread inward. If the disease becomes severe, the leaves may dry out, wilt, and eventually fall off. When this happens, pepper plants lose their photosynthetic ability, leading to overall weakness, reduced yield, and lower pepper quality.
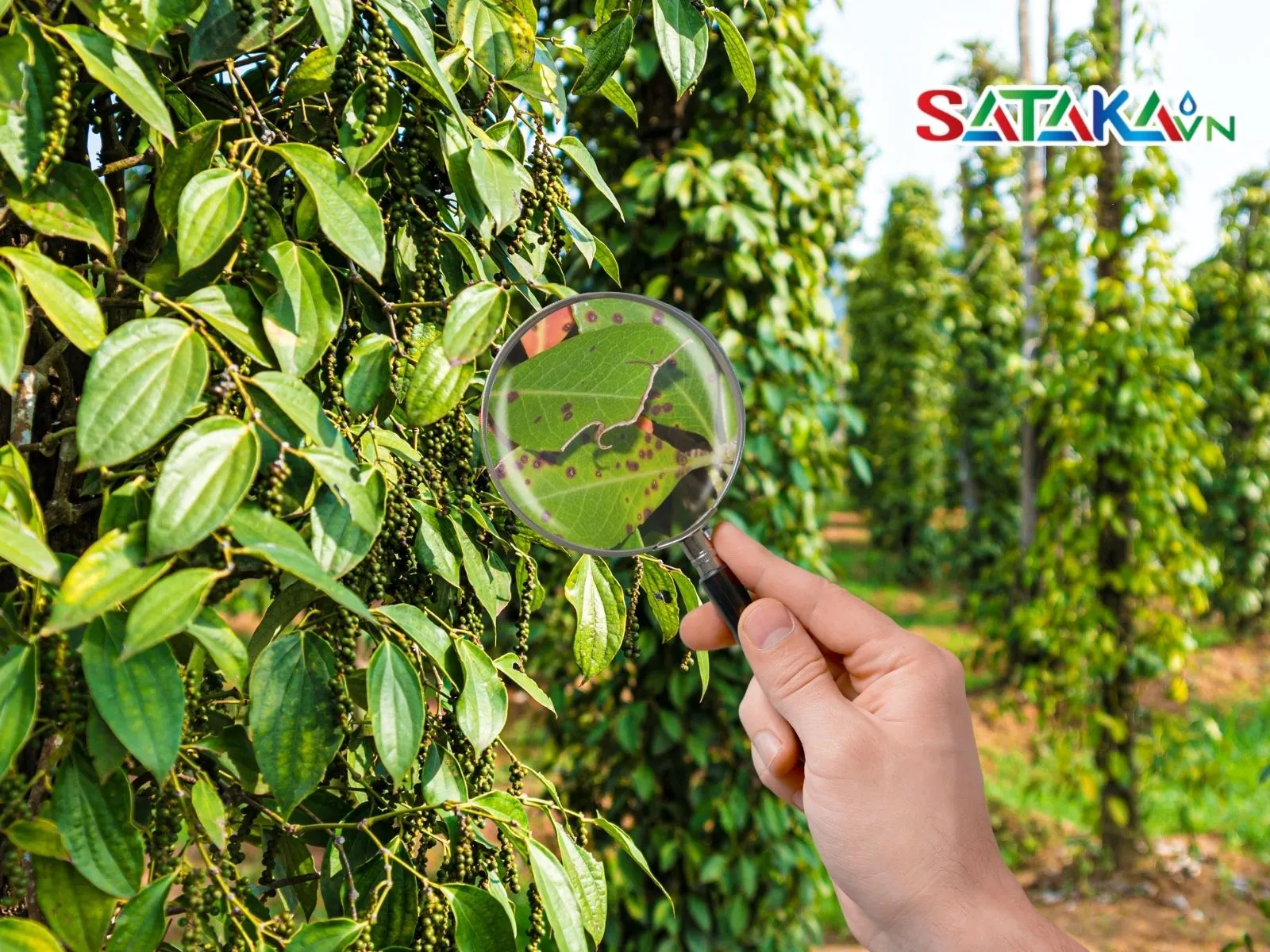

Brown spots on leaves
If not treated promptly, the disease can spread to the entire canopy, making treatment more difficult. Especially in humid and high-temperature conditions, leaf spot disease can spread rapidly among plants in the same area, significantly reducing pepper harvest yields.
The primary causes of leaf spot disease on pepper plants are fungi and bacteria, most commonly Colletotrichum fungi and certain bacteria. These fungi thrive in wet and warm environments, especially during the rainy season. When fungi or bacteria come into contact with the plant, they infiltrate leaf tissues and cause damage. Initially, these damages appear as small yellow spots that eventually spread and darken.
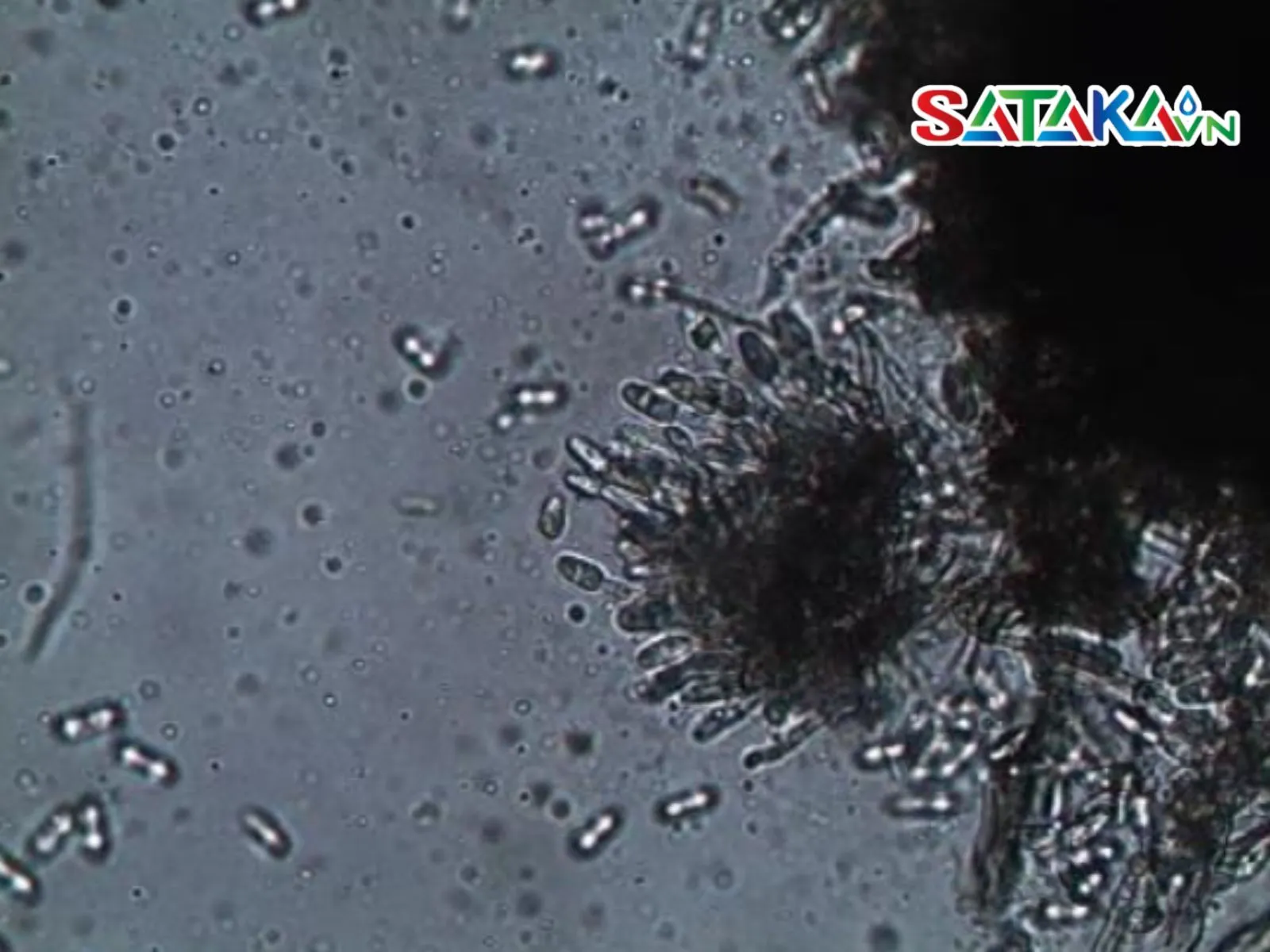
Colletotrichum mushroom
Environmental conditions also play a significant role in the development of the disease. Areas with high humidity, heavy rainfall, or poor soil drainage create ideal conditions for fungi and bacteria to thrive. Additionally, dense planting, insufficient sunlight, and poor ventilation contribute to the rapid spread of the disease.
Leaf spot disease not only directly harms the plant's leaves but also significantly impacts the growth and productivity of pepper plants. When the disease occurs, the plant's photosynthetic process is disrupted, preventing it from generating enough energy for normal growth. This leads to reduced plant vitality, making it more susceptible to other diseases.

Tree vitality decreases
More seriously, leaf spot disease can considerably lower harvest yields. Infected pepper plants produce lower-quality peppercorns that are uneven in color and fail to meet commercial standards, reducing the economic value of the product. For households growing pepper for income, leaf spot disease can be a significant shock, causing substantial financial losses.
Preventing the disease from the start is always the most effective and economical approach. To prevent leaf spot disease, farmers should implement proper agricultural practices such as improving the drainage system in pepper gardens to avoid stagnant water after rain. Planting at appropriate densities ensures adequate light and air circulation, reducing the risk of disease. Additionally, pruning branches and leaves is essential for increasing ventilation, thereby limiting the spread of fungi and bacteria.
If leaf spot disease is already present, using plant protection products is necessary. Fungicides containing active ingredients such as Chlorothalonil, Carbendazim, Azoxystrobin, or Mancozeb are commonly recommended to control leaf spot disease. However, for optimal effectiveness, farmers should strictly follow the correct dosage and spraying schedule to avoid overuse, which could harm the environment and crops.

The active ingredient Azoxystrobin can prevent leaf spot disease
In addition to chemical treatments, biological methods are increasingly favored for their safety and long-term effectiveness. Farmers can use biological products containing beneficial microorganisms to prevent and control leaf spot disease on pepper plants. Combining biological methods with proper agricultural practices helps protect pepper plants in the long term, minimizing negative impacts on the environment and human health.
To ensure healthy growth and reduce diseases, monitoring the health of pepper plants daily is crucial. Farmers should regularly inspect plants to detect early disease signs and treat them promptly. Additionally, providing sufficient nutrition to the plants is essential for enhancing their resistance to fungal and bacterial invasion.
Foliar fertilizers containing trace elements and microorganisms should be used correctly to improve the photosynthetic ability and growth of pepper plants. Moreover, pruning branches and leaves and maintaining good ventilation in the garden help prevent the spread of leaf spot disease.

Add foliar fertilizer
Leaf spot disease on pepper plants is a serious issue that requires timely treatment. Always pay attention to proper care for pepper plants and adopt preventive measures to maintain a healthy and productive pepper garden.
This article by Sataka provides detailed information about leaf spot disease on pepper plants and practical methods suitable for farmers and those interested in protecting and caring for pepper plants.