What are organophosphate pesticides? Organophosphate pesticides contain organic compounds of phosphorus, which are widely used to control insect pests in agriculture.
Organophosphate Group
Organic phosphate insecticides are among the most widely used plant protection chemicals in modern agriculture. With their ability to control a wide range of pests, these insecticides have become essential tools for maintaining the health and productivity of crops. In this article, Sataka Vietnam delves into the world of organic phosphate insecticides. Let's explore how they can effectively support you in protecting your crops!
1. Overview of Organic Phosphate Insecticides
1.1 What Are Organic Phosphate Insecticides?
Organic phosphate insecticides (commonly known as organophosphates) are plant protection chemicals with superior pest control properties. These products contain phosphorus (P) groups and are often esters derived from phosphoric acid. They are known for their shorter half-life compared to organochlorines, making them a popular choice for pest management in agriculture.
1.2 Chemical Composition
Organic phosphate insecticides have a unique chemical structure that includes fundamental elements such as Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S), and Phosphorus (P). These compounds are typically organic derivatives of phosphoric acid, designed to effectively eliminate pests and diseases.
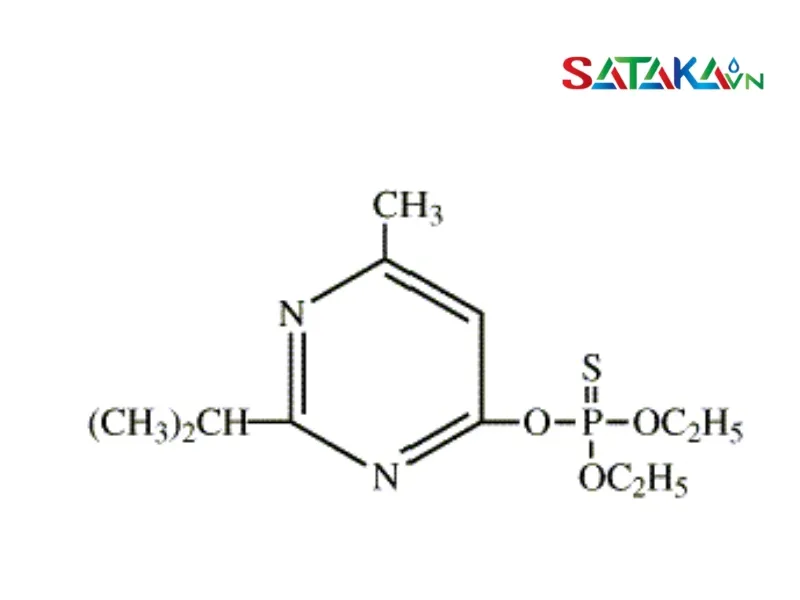
Structural structure of the organophosphate group
1.3 Characteristics of Organic Phosphate Insecticides
These insecticides possess several key features, making them indispensable tools for crop protection:
- Contact and Penetration: Organic phosphate insecticides penetrate the body of pests through the skin or digestive system, delivering toxic effects directly.
- Ingested Toxicity: When sprayed or applied to crops, pests ingest the insecticide through food sources like leaves or stems, causing harm via the digestive system.
- Fumigation Effects: Some types can produce gases, smokes, or mists, effectively controlling not only pests but also fungi, bacteria, and rodents.
- Systemic Action: These insecticides can move within the plant to effectively target pests.
2. Mechanism of Action
Organic phosphate insecticides work by inhibiting the Cholinesterase enzyme, which is responsible for breaking down Acetylcholine in the nervous system. When the enzyme is inhibited, Acetylcholine accumulates, overstimulating the nervous system. This leads to muscle weakening, paralysis, and ultimately the death of the pest.
3. Applications and Main Active Ingredients
3.1 Applications
- Control of Various Pests: Effective against insects like caterpillars, aphids, thrips, and other harmful pests.
- Crop Protection: Safeguards crops from germination to harvest, ensuring high yields and quality produce.
- Indoor and Outdoor Use: Suitable for greenhouses, orchards, and outdoor crops to manage pest populations.

Main uses of organophosphate pesticides
3.2 Main Active Ingredients
- Parathion: A powerful active ingredient used for controlling pests on cotton, rice, and fruit crops. While Parathion Ethyl is banned, Parathion remains effective for other applications.
- Malathion: Popular for controlling mites, fleas, and mosquitoes, and effective on fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
- Dichlorvos: Ideal for managing fungus gnats, aphids, mites, and caterpillars in greenhouses and outdoor crops.
- Chlorpyrifos: Targets termites, mosquitoes, and worms, and is used on crops, livestock, and in buildings.
- Profenofos: Effective against eggs, larvae, and adult pests like caterpillars, mites, and stink bugs.
- Fenitrothion: Commonly used to control stem borers, mealybugs, and other harmful insects.
3.3 Groups of Organic Phosphate Insecticides
- Insecticides: Target harmful pests on crops.
- Fungicides: Combat fungal and bacterial diseases.
- Herbicides: Manage and eliminate weeds.
4. Are Organic Phosphate Insecticides Harmful?
4.1 Environmental Impact
Organic phosphate insecticides degrade quickly in the environment due to sunlight, water, and microorganisms. However, proper application is crucial to prevent contamination of soil and water sources.

Use medicine properly and have protective gear for safety
4.2 Human Safety
These insecticides can be highly toxic to warm-blooded animals, including humans and livestock. They may enter the body via inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact.
Acute Toxicity Symptoms:
- Fatigue and skin irritation
- Headaches, nausea, and vomiting
- Dizziness, insomnia, and blurred vision
- Increased salivation and tear production Severe cases, particularly involving substances like Methyl Parathion and Parathion Ethyl (now banned), can be fatal.
5. Precautions for Using Organic Phosphate Insecticides
- Avoid Overdosing: Always follow recommended dosages to maintain crop quality and safety. Overuse can harm plants and the environment.
- Source Reliable Products: Use certified products from reputable suppliers and avoid banned substances.
- Apply Evenly: Ensure even distribution, especially in areas with high pest populations.
- Prepare Proper Dilutions: Mix the insecticide according to the instructions, balancing the amounts of water and product.
- Use at the Right Time: Apply insecticides during early pest infestations, preferably in the morning or evening when temperatures are cooler.
- Wear Protective Gear: Use gloves, masks, and goggles to protect yourself and others.
- Store Safely: Keep insecticides in dry, cool areas away from children and animals, ensuring packaging remains intact.

Through this article, we hope you’ve gained a deeper understanding of organic phosphate insecticides and their applications in agriculture. While they are highly effective in pest control, it is crucial to use them safely to protect both human health and the environment.
For tailored advice and solutions, feel free to contact Sataka Vietnam!



