Sataka's article provides detailed information about rust disease on pepper plants, including symptoms, causes and prevention, helping people handle the disease promptly.
To protect your pepper plantations from rust disease, it is essential to understand the symptoms, causes, and methods for prevention and treatment. This article by Sataka provides detailed information about the disease, helping farmers take timely and effective measures.
Rust disease in pepper plants is primarily caused by a fungus called Hemileia vastatrix. This fungus primarily parasitizes the leaves of pepper plants and can rapidly develop under favorable environmental conditions. The disease thrives in tropical, humid climates with temperatures ranging from 20°C to 28°C, especially during the rainy season.
Key factors promoting the development of the disease include:
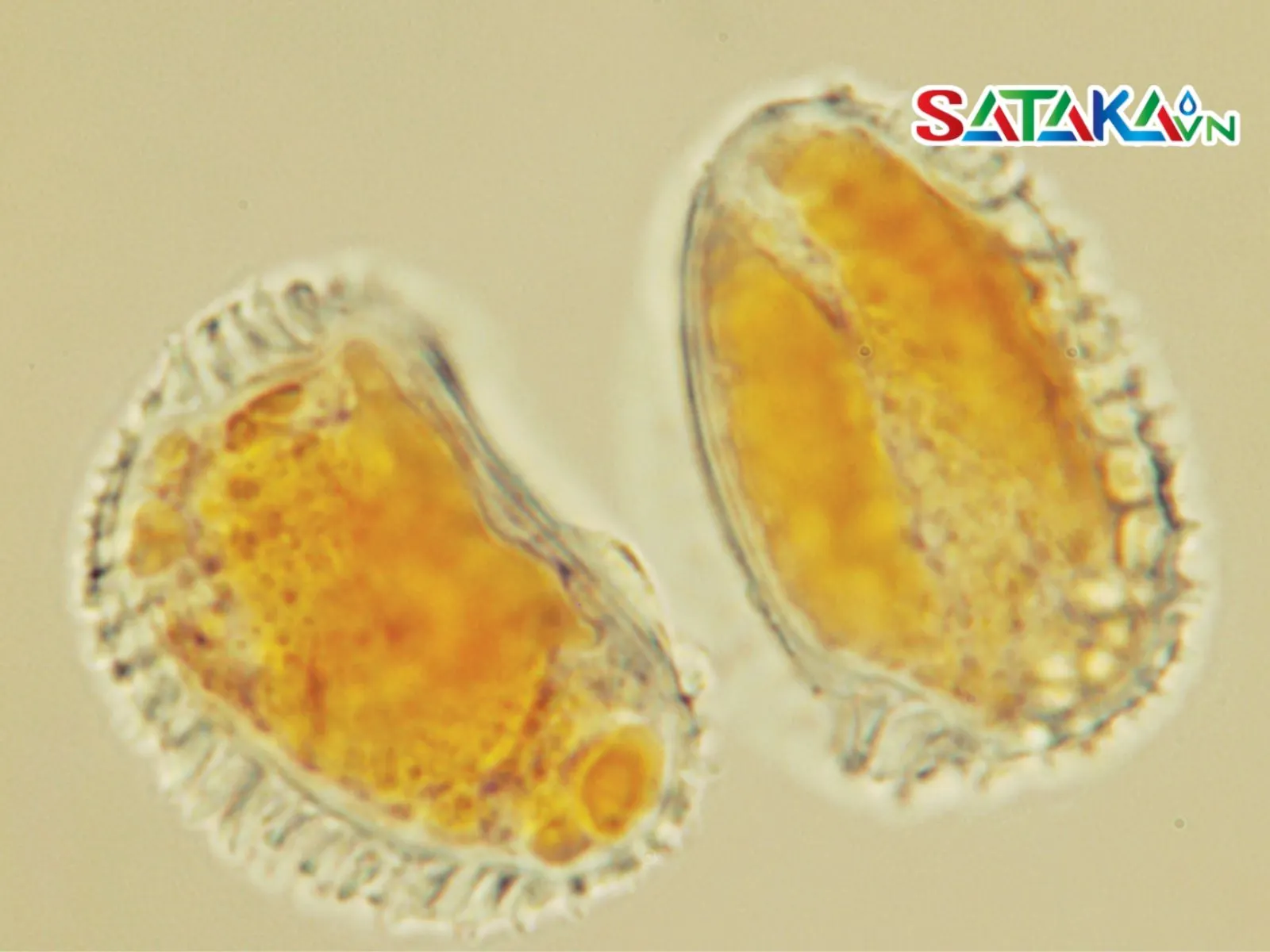
Hemileia Vastatrix mushroom
Early detection of rust disease is critical for timely intervention. The symptoms can be easily recognized on the leaves, stems, and even fruits of pepper plants.
The initial symptoms usually appear on the underside of the leaves as small yellow-orange spots, which gradually turn reddish-brown, resembling rust. These spots tend to spread, causing the leaves to dry out and fall prematurely. Severely infected leaves may become deformed, curled, and lose their ability to photosynthesize.
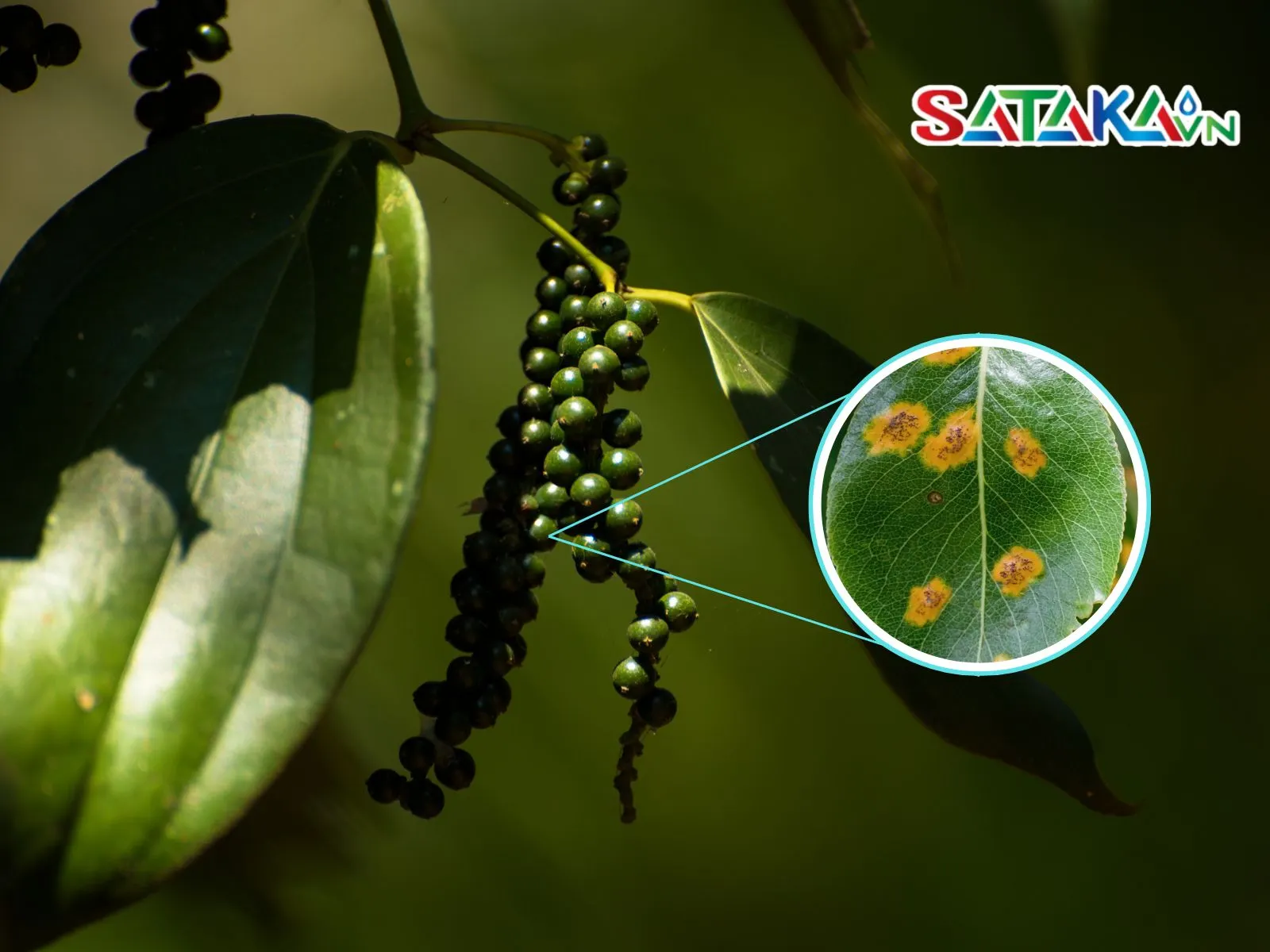

How to detect rust disease on pepper leaves
Infected plants may exhibit weakened growth, with dry branches and uneven leaf development. In severe cases, the branches may die back gradually, reducing the plant’s vitality.
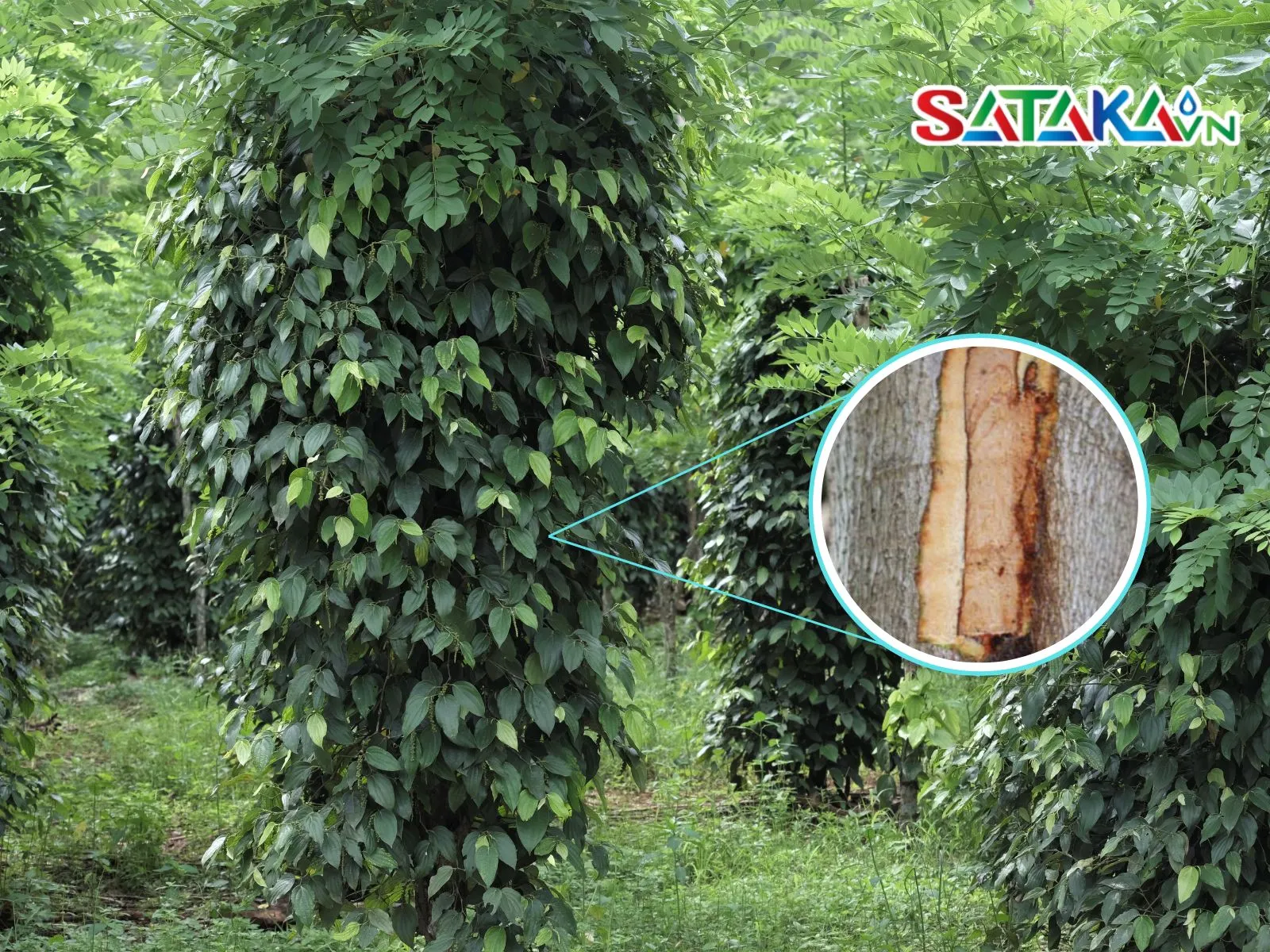

How to detect rust disease on pepper tree branches
Rust disease can also affect pepper fruits, particularly young ones. Infected fruits are prone to early drop, reducing the yield during harvest.
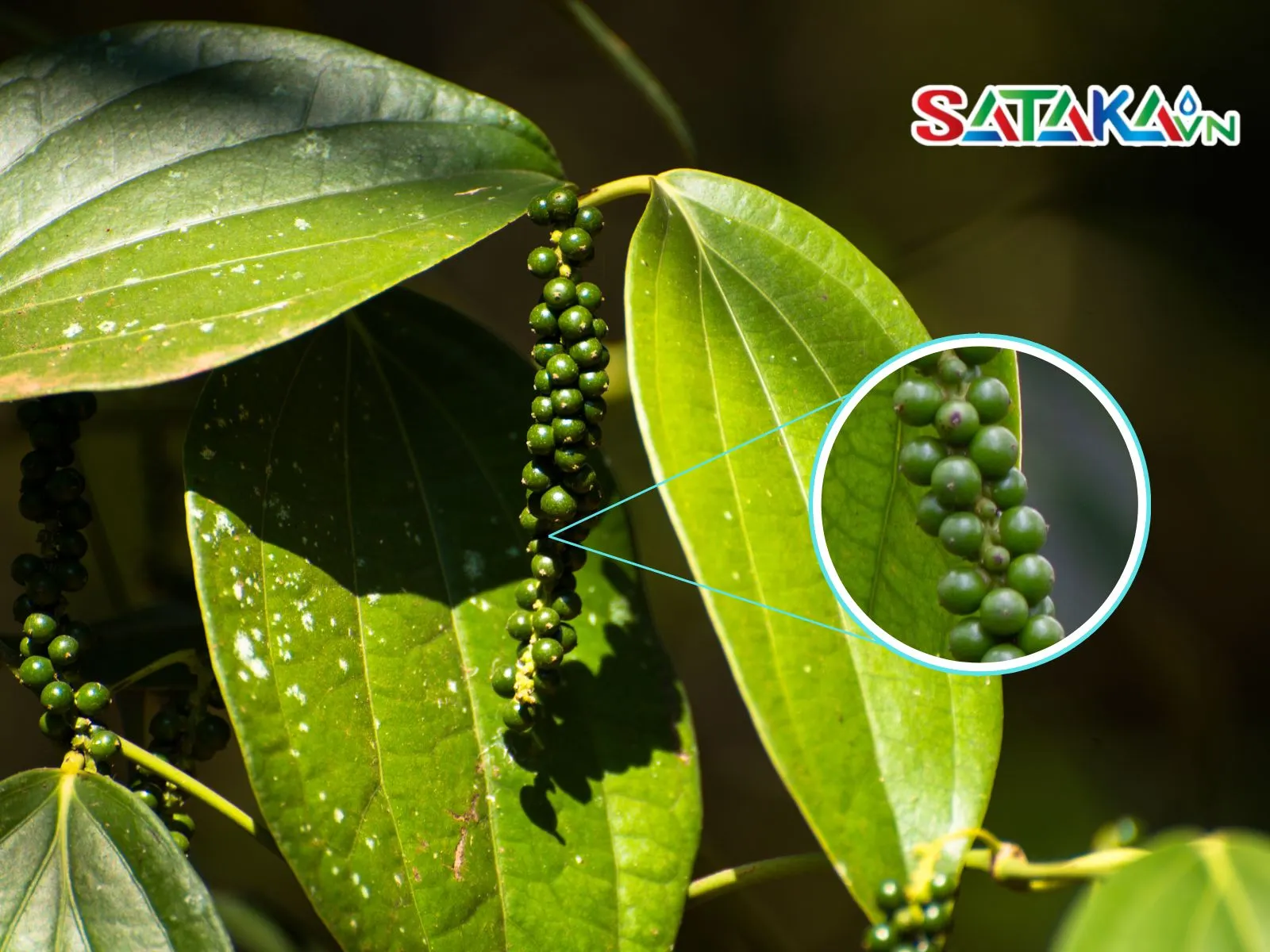

How to detect rust disease on pepper fruits
Rust disease not only directly affects the health of pepper plants but also causes significant economic losses for farmers.
One of the most severe consequences of rust disease is reduced yield. When leaves fall off, the plant loses its ability to photosynthesize effectively, resulting in poor growth and reduced fruit production.
If not treated promptly, the disease can affect the entire plant, leading to reduced productivity in subsequent seasons. This highlights the importance of early detection and treatment.

Reduced output
Prevention is better than cure, so applying preventive measures is crucial to avoid the spread of rust disease in pepper plants.

Reasonable distance for planting trees
If your pepper plants are already infected with rust disease, timely and appropriate measures are necessary to limit its spread and minimize damage.
Apply fungicides containing active ingredients such as Mancozeb, Hexaconazole, or Propiconazole to prevent and treat rust disease in pepper plants. Fungicide applications should be done periodically and according to agricultural experts’ recommendations to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Use biological products or foliar fertilizers that enhance the plant’s resistance to fungal attacks. This helps the plant combat the disease more effectively.
Promptly remove and dispose of infected leaves and branches to prevent the disease from spreading. Heavily infected parts should be destroyed away from the plantation to eliminate sources of infection.

Use antifungal medication containing the active ingredient Propiconazole
The rainy season is when rust disease develops most actively, so farmers need to pay special attention to managing their plantations during this period.
Rust disease in pepper plants is one of the most common and dangerous diseases farmers face. By proactively caring for the plants, creating a healthy growing environment, and implementing protective measures, farmers can effectively safeguard their plantations from rust disease. Sataka hopes this article benefits farmers, helping their pepper plants grow healthily, ensuring good yields and quality for the harvest, and improving economic outcomes.