Discovery of the important compound ergosterol in mushrooms, with applications in vitamin D2 production, antifungal drugs, and pharmaceutical research.
Ergosterol is an essential compound found primarily in fungi and plants, with numerous practical applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food production. Not only is it vital for maintaining the structural integrity of fungal cell membranes, but it also contributes to the production of vitamin D2, antifungal drug development, and other industrial and research applications. In this article, Sataka explores the key aspects of ergosterol, from its definition and origins to its applications and environmental impact.
Ergosterol is an important organic compound commonly found in the cell membranes of fungi and some plants. Essentially, ergosterol is a sterol, similar to cholesterol in animals, that plays a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of fungal cell membranes. It not only enhances the flexibility of the cell membrane but also affects its permeability, ensuring efficient cell activity.

Ergosterol is a white powder
When discussing ergosterol, it is important to highlight its distinction from cholesterol. While both serve similar functions in supporting cell membrane structure, ergosterol is primarily found in fungi and plants, whereas cholesterol is prevalent in animal cells. This difference underscores the unique role of ergosterol across various industries, from food production to pharmaceuticals.
Ergosterol is predominantly found in fungi and some plants, where it plays an essential role in their cell membrane structure. Its distribution extends beyond natural environments to numerous industrial and scientific applications.
Ergosterol is mainly produced by fungi, including yeast and molds. It is notably present in economically valuable fungi such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, commonly used in beer and wine production. While some plants also contain ergosterol, their concentrations are much lower compared to fungi.
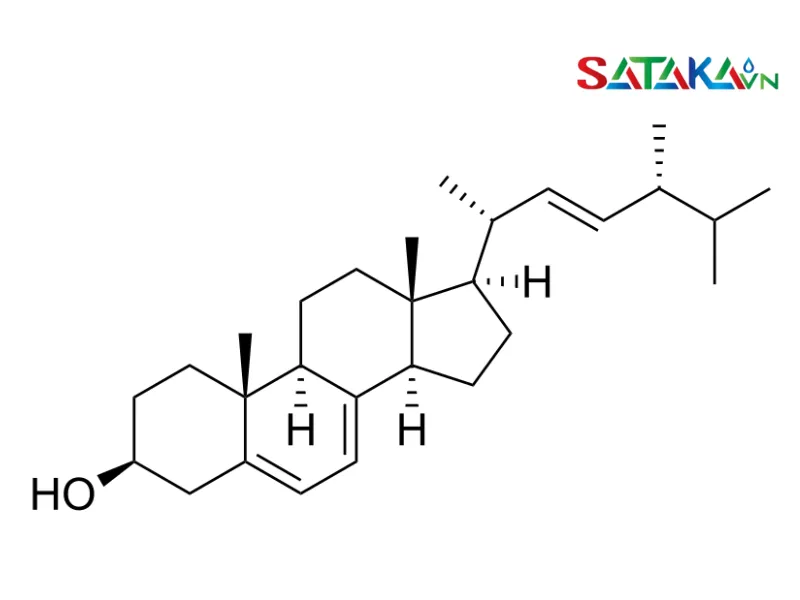
Chemical structure of Ergosterol
Ergosterol is concentrated in fungal cell membranes, where it is crucial for maintaining membrane integrity and function. It can also be found in processed fungal products such as dried mushrooms, fungal extracts, and yeast derivatives.
In industrial applications, ergosterol is extracted from fungi and utilized in fields ranging from food to pharmaceuticals. For example, it is a key compound in antifungal drug development and can be converted to vitamin D2 when exposed to light.
One of ergosterol’s primary functions is to maintain the structure and flexibility of fungal cell membranes. Similar to cholesterol in animals, ergosterol enhances membrane stability by modulating its rigidity and flexibility.
Ergosterol plays a significant role in controlling the permeability of fungal cell membranes. It facilitates the efficient exchange of nutrients and essential molecules between the cell and its surroundings while eliminating metabolic byproducts and toxins.
A unique function of ergosterol is its ability to convert to vitamin D2 when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This process occurs when ergosterol in fungi interacts with sunlight or UV light, resulting in the production of vitamin D2. This vitamin is essential for bone health and immune system support.
Ergosterol is a target for many antifungal drugs. These drugs, such as azoles and polyenes, inhibit ergosterol synthesis, thereby weakening and destroying fungal cells. Understanding ergosterol's functions is crucial for developing effective treatments for fungal infections.
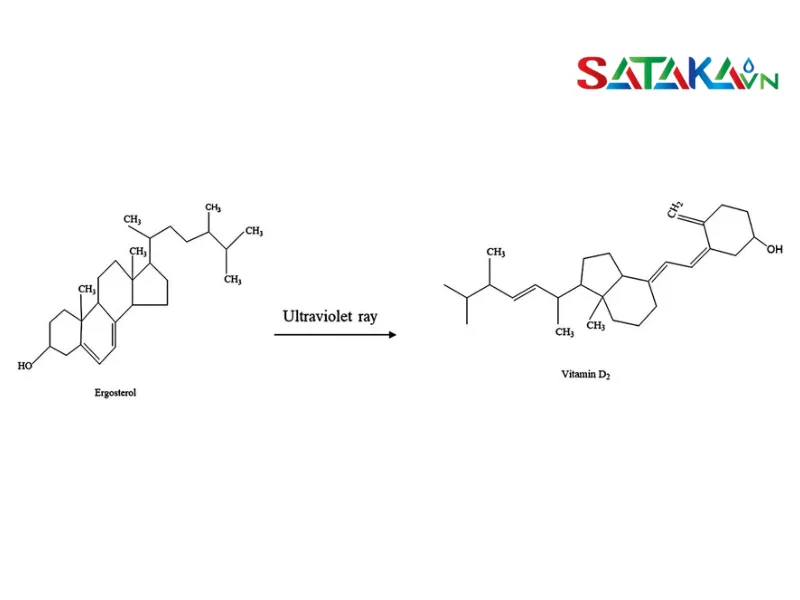
Ergosterol has the ability to convert into vitamin D2
Ergosterol is widely used in the food industry, especially in products derived from fungi. Extracted from fungi, ergosterol can be used to develop functional foods and dietary supplements. Additionally, it enhances the nutritional value of processed fungal products, providing added health benefits.
In pharmaceuticals, ergosterol is a key component in developing antifungal drugs. Many antifungal medications, such as azoles and polyenes, work by targeting ergosterol synthesis, thereby eliminating fungal cells. Understanding ergosterol has enabled researchers to create more effective treatments for fungal infections.
Moreover, ergosterol is being explored in cancer treatment research and the development of medications for other diseases. These studies may lead to the discovery of new compounds with potential applications in disease prevention and treatment.
Vitamin D2 Production: One of the most prominent applications of ergosterol is in producing vitamin D2. When exposed to UV light, ergosterol from fungi is converted into vitamin D2, which is an important ingredient in dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals. This process significantly benefits bone health and immune system functionality.
Antifungal Drug Development: Ergosterol is the primary target of many antifungal drugs. Medications like azoles and polyenes inhibit ergosterol synthesis, leading to weakened fungal cells and their eventual destruction.
Cancer Research and Drug Development: Recent research has investigated ergosterol's potential in cancer treatment. Studies suggest that ergosterol may inhibit cancer cell growth and enhance the efficacy of existing therapies.
Cosmetic Industry Applications: Ergosterol is also used in the cosmetic industry for its antioxidant and moisturizing properties. Skincare products containing ergosterol can improve skin elasticity and reduce signs of aging.
Ergosterol not only affects biological processes within cells but also has significant environmental implications. Understanding these impacts is essential for evaluating its influence on ecosystems and implementing proper management and protection measures.
Impact on Fungal Ecosystems: Ergosterol is a critical component of fungal cell membranes, and variations in its concentration can affect fungal ecosystems. Research shows that changes in ergosterol levels influence fungal growth and activity, which in turn impacts plants and animals dependent on fungi in the ecosystem.
Effects of Antifungal Compounds: The widespread use of antifungal drugs targeting ergosterol can negatively affect the environment. These drugs may harm non-target fungal species and organisms that rely on fungi.
Role in Organic Matter Decomposition: Ergosterol contributes to the decomposition of organic matter in soil through fungi. Changes in ergosterol levels can affect fungal decomposition capabilities, influencing soil quality and plant growth.
Impact of Processed Fungal Products: Products containing ergosterol can also impact the environment if improperly managed. Unregulated disposal of these products may cause pollution and harm ecosystems.
With these insights, you can use ergosterol effectively and sustainably, contributing to industrial advancements while protecting the environment. Sataka specializes in providing chemical raw materials, pesticides, and pest control solutions tailored to your needs. Contact Sataka today for more information!