What are pyrethroids? Pyrethroids are a group of synthetic chemicals based on pyrethrin, a natural insecticide found in chrysanthemums, often used in mosquito and insecticides.
Have you ever wondered what ingredients in the insecticides you use daily cause such immediate effects on insects, making them die instantly? In this article, Sataka will help you better understand pyrethroids. From the characteristics of pyrethroid insecticides and their mechanisms of action to safe usage practices and practical applications, let’s explore the details together!
Pyrethroids are synthetic insecticides developed based on natural compounds called pyrethrins, which are extracted from chrysanthemum flowers. Pyrethroid compounds are designed to be more long-lasting and potent compared to natural pyrethrins. In other words, pyrethroids are artificial chemicals engineered to enhance the effectiveness of insecticides while addressing the limitations of pyrethrins.
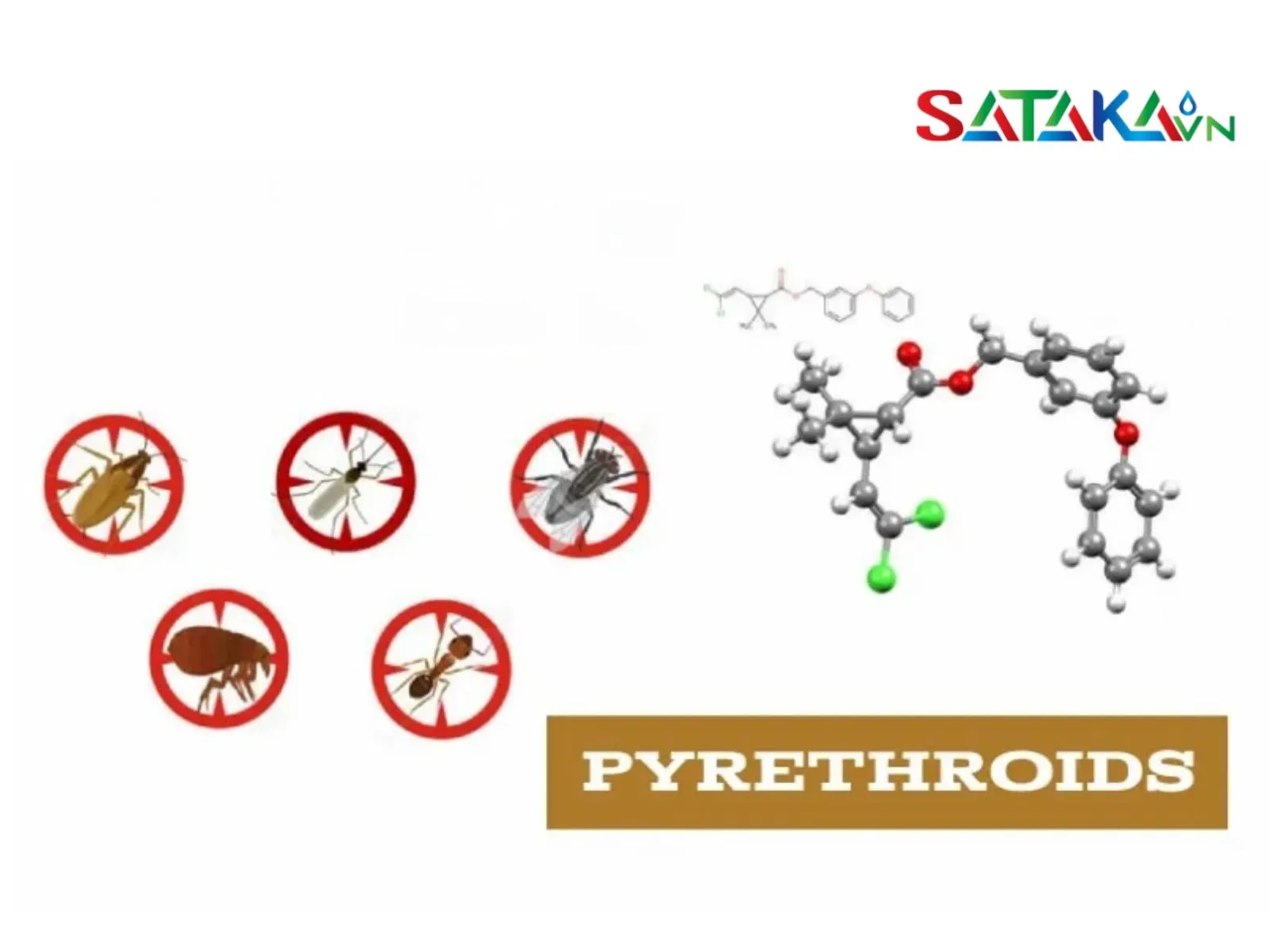
Join Sataka to learn about what Pyrethroids are?
Pyrethroids are known for several key features:
High efficacy against insects: Pyrethroids are highly effective in eliminating pests like mosquitoes, fleas, flies, moths, and ants, making them invaluable for crop protection and pest control.
Stability and durability: Unlike natural pyrethrins, pyrethroids remain active for longer periods under sunlight and environmental exposure.
Selective action: While pyrethroids affect a broad range of insects, products derived from these chemicals are often developed to minimize impacts on humans and other animals.
Evolution from pyrethrins: Pyrethroids improve on pyrethrins by enhancing effectiveness and reducing the need for frequent applications.
Pyrethroids primarily act on the nervous system of insects, specifically targeting the neurons in their bodies. Here’s how they perform their insecticidal function:
Impact on the nervous system: Pyrethroids enter an insect’s body through ingestion or direct contact. Once inside, they disrupt the function of ion channels in the insect’s nerve cells.
Targeting sodium ion channels: Pyrethroids bind to sodium ion (Na⁺) channels on nerve cell membranes, preventing them from opening or functioning properly.
Interrupting nerve transmission: By affecting sodium ion channels, pyrethroids interfere with the transmission of neurotransmitters between nerve cells, halting communication between muscles and organs.
Resulting paralysis and death: The disruption of nerve signals causes paralysis, rendering insects unable to move, feed, or survive.
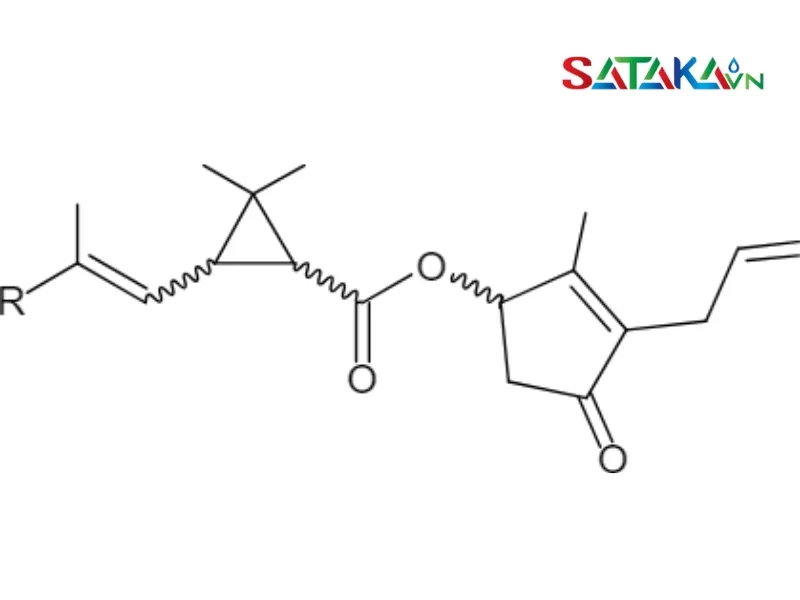
Main uses of Pyrethroid
Pyrethrins: Naturally derived and used in household insecticides for temporary pest control due to their quick action.
Pyrethroids: Favored in specialized applications such as agricultural pesticides and long-lasting pest control products due to their stability and extended efficacy.
| Criteria | Pyrethrin | Pyrethroids |
| Source | Natural, extracted from chamomile | Synthesized and developed from Pyrethrin |
| Chemical structure | Simple, includes Pyrethrin I and Pyrethrin II | More complex, consisting of many different compounds |
| Effective in killing insects | Kill insects quickly | Kills insects effectively and for a long time |
| Time of effect | Short-term, easily decomposed by light and temperature | Long-term, more sustainable under the impact of the environment |
| Application | Often used in basic insecticide products | Used in many specialized insecticide products |
Before using any product containing pyrethroids, carefully read the instructions. These guidelines provide critical information about preparation, application, and safety measures. Follow them closely to achieve optimal results and minimize risks.
When handling pyrethroids, wearing protective clothing is crucial to safeguard against potential hazards:
Helmet and protective suit: Protect your body from direct exposure to chemicals.
Gloves and safety glasses: Use gloves and safety glasses to protect your skin and eyes from contact with pyrethroids.
Full-body protective gear: For prolonged exposure, wear full-body protective suits.
To use pyrethroids safely, prevent contact with your skin and eyes. If accidental exposure occurs:
Immediate washing: Rinse thoroughly with clean water and saline solution.
Handwashing: Wash hands and exposed areas with soap and water after handling products.

Please read Pyrethroid products carefully before using
Store pyrethroids appropriately to maintain safety and product effectiveness:
Cool, dry place: Keep products in a dry, cool area, away from direct sunlight.
Out of reach: Ensure they are stored out of the reach of children and pets.
Clean storage area: Keep the storage space clean and free of contaminants.
Adhering to recommended dosages ensures effective and safe use:
Correct dosage: Follow the product's label instructions for the appropriate amount.
Avoid overuse: Using more than the recommended amount won’t increase effectiveness but could harm health and the environment.
Agriculture: Protecting crops, managing weeds, and preserving food supplies.
Healthcare: Controlling pests, preventing infectious diseases, and caring for pets.
Environmental management: Outdoor pest control and ecosystem protection.
Industrial and production use: Manufacturing insecticides, managing pests in food production, and producing health protection products.
Consumer goods: Household products, pet care, and hygiene solutions.
When exposed to pyrethroids, the following nervous system-related symptoms may occur:
Headaches: Frequent and severe headaches.
Fatigue: A sense of exhaustion and loss of energy.
Seizures: In severe cases, convulsions may occur.
Anxiety: Feelings of unease or unexplained fear.
Discomfort: General feelings of uneasiness or restlessness.
Symptoms affecting the circulatory and respiratory systems may include:
Rapid heartbeat: Increased heart rate and palpitations.
Irregular pulse: A sensation of irregular or fast pulse.
Difficulty breathing: Feeling unable to breathe properly.
Coughing: Either dry coughing or coughing with mucus.
Chest discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the chest area.
Contact with pyrethroids can lead to the following skin and eye-related symptoms:
Redness and pain: Skin irritation and soreness from exposure.
Burning sensation: A feeling of heat or burning on the skin.
Sudden lack of sweating: Abrupt reduction or cessation of sweating.
Eye pain: Pain or redness in the eyes.
If these symptoms occur, immediately wash the affected area with clean water and saline solution.
Digestive symptoms resulting from exposure to pyrethroids include:
Digestive issues: Abdominal discomfort and nausea.
Diarrhea: Loose stools and uncontrollable diarrhea.

Through this article, we hope you now have a clear understanding of “What are Pyrethroids?” and the essential information related to these insecticides. From their mechanism of action and symptoms of poisoning to safe usage practices, we’ve covered various aspects.
If you have further questions about pyrethroids or need advice on insecticides and pest control products, don’t hesitate to contact us at Sataka Vietnam. We’re always here to help!