What is the triazole group? The triazole group includes compounds containing a 5-membered ring with three nitrogen atoms, often used in fungicides and some medicines.
Did you know that the triazole group not only plays a vital role in protecting crops from fungal diseases but is also an indispensable part of crop disease management strategies? In this article, Sataka provides a comprehensive overview of the triazole group, helping you understand its characteristics, classifications, applications, and how to use triazole-based products effectively for the best results.
The triazole group refers to a class of special chemical compounds widely recognized for their role in treating and preventing fungal diseases in crops. These compounds feature a triazole structure, consisting of three nitrogen atoms and two carbon atoms within a ring. This structure makes triazoles highly effective at inhibiting the growth of fungi that harm plants.
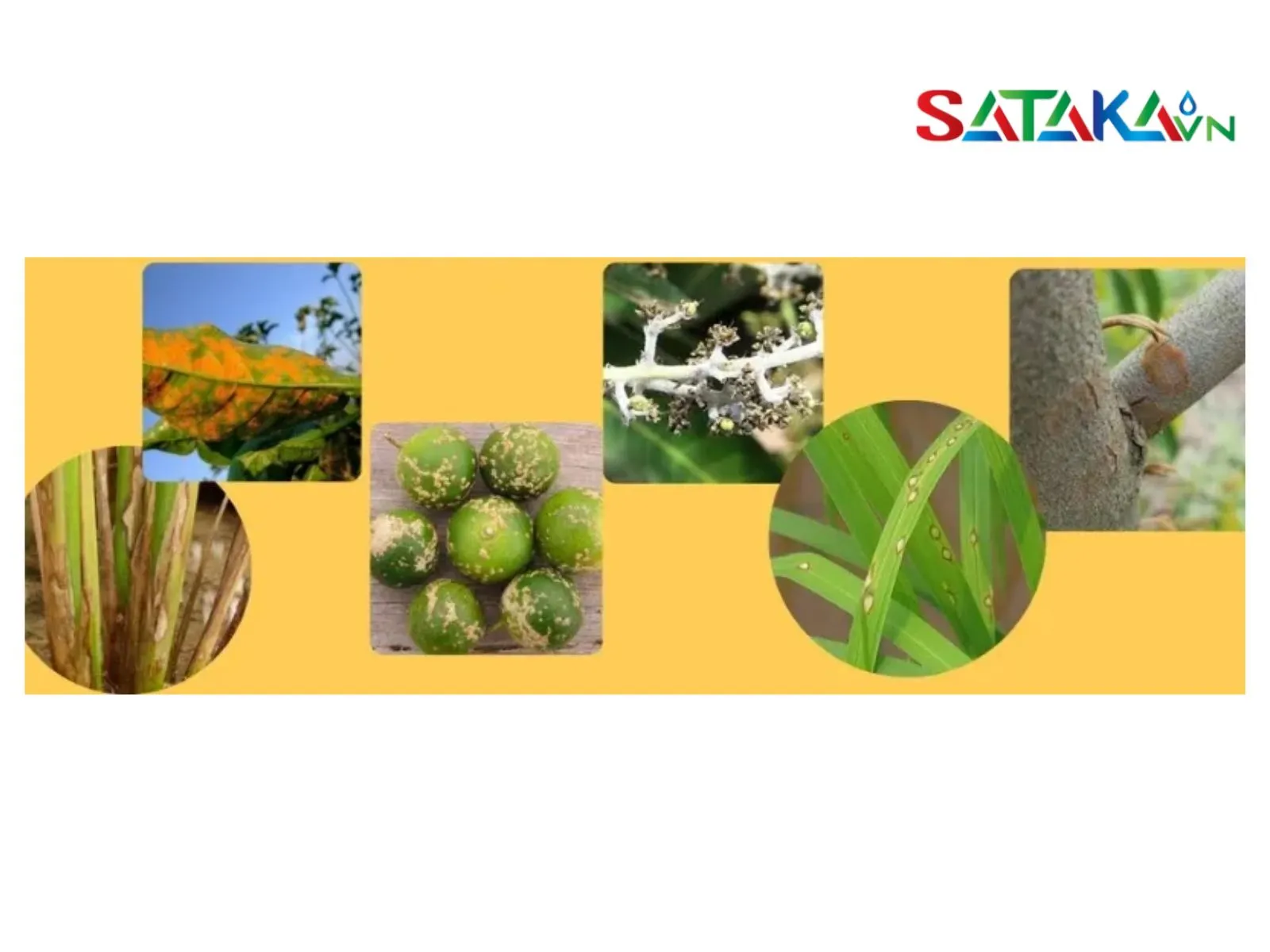

Triazoles are primarily used in antifungal treatments within agriculture. They function by disrupting the synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. This mechanism helps control fungal development and protects crops from common diseases like black spot, powdery mildew, and downy mildew.
Distinctive Chemical Structure:
Triazoles are characterized by their triazole ring structure, which contains three nitrogen atoms and two carbon atoms. This structure allows strong binding with fungal enzymes, effectively inhibiting their growth. It also makes triazoles a preferred choice in antifungal treatments.
Efficient Mechanism of Action:
Triazoles inhibit the enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase, which is crucial for ergosterol synthesis in fungi. Without ergosterol, fungal cell membranes fail to function normally, leading to fungal death.
High Selectivity:
Triazoles exhibit high selectivity, targeting fungal cells while sparing plant cells. This minimizes side effects on crops and ensures that triazole-based products effectively combat fungi without harming plants.
High Stability:
Triazole compounds maintain their antifungal efficacy under various environmental conditions, including heavy rain and high temperatures. This stability is a key reason for their widespread use in agricultural antifungal products.
1,2,4-Triazole:
This structure features nitrogen atoms at positions 1, 2, and 4 on the triazole ring. Compounds in this group, such as fluconazole and itraconazole, are commonly used in antifungal products for treating plant diseases.
1,2,3-Triazole:
Here, nitrogen atoms are arranged at positions 1, 2, and 3. Compounds like metconazole and prothioconazole in this group are known for their ability to combat various fungal pathogens.
Fungal Disease Treatment:
Compounds like propiconazole and difenoconazole are used to treat specific fungal diseases, including black spot, powdery mildew, and downy mildew.
Preventive Treatments:
Compounds such as tebuconazole and bixafen are designed for preventive use to avoid fungal infections. These products are often applied on a schedule to protect crops from potential fungal threats.
Broad-Spectrum Antifungal Compounds:
Azoxystrobin and fluopyram are examples of broad-spectrum triazoles effective against multiple fungal diseases.
Selective Antifungal Compounds:
Cyproconazole and epoxiconazole target specific fungal diseases, leaving other fungi and crops unaffected. They are often included in targeted antifungal treatments.
Long-Acting Compounds:
Compounds like flutriafol and tebuconazole provide prolonged protection when sprayed on crops.
Fast-Acting Compounds:
Propiconazole and difenoconazole offer immediate effects, quickly eradicating fungi and preventing disease spread.
Triazole-based compounds are found in a variety of agricultural products, including:
Sataka is a trusted supplier of agricultural chemicals, including triazole-based plant protection products, widely favored by customers. Contact us for professional advice tailored to your needs!

Sataka Vietnam hopes this article has provided you with valuable insights into the triazole group and its applications in crop care. From understanding what triazoles are to exploring their features, classifications, and effective usage, we aim to deliver the most detailed and helpful information.
By using triazole-based products correctly, you can protect your crops from fungal diseases and contribute to sustainable agricultural development.